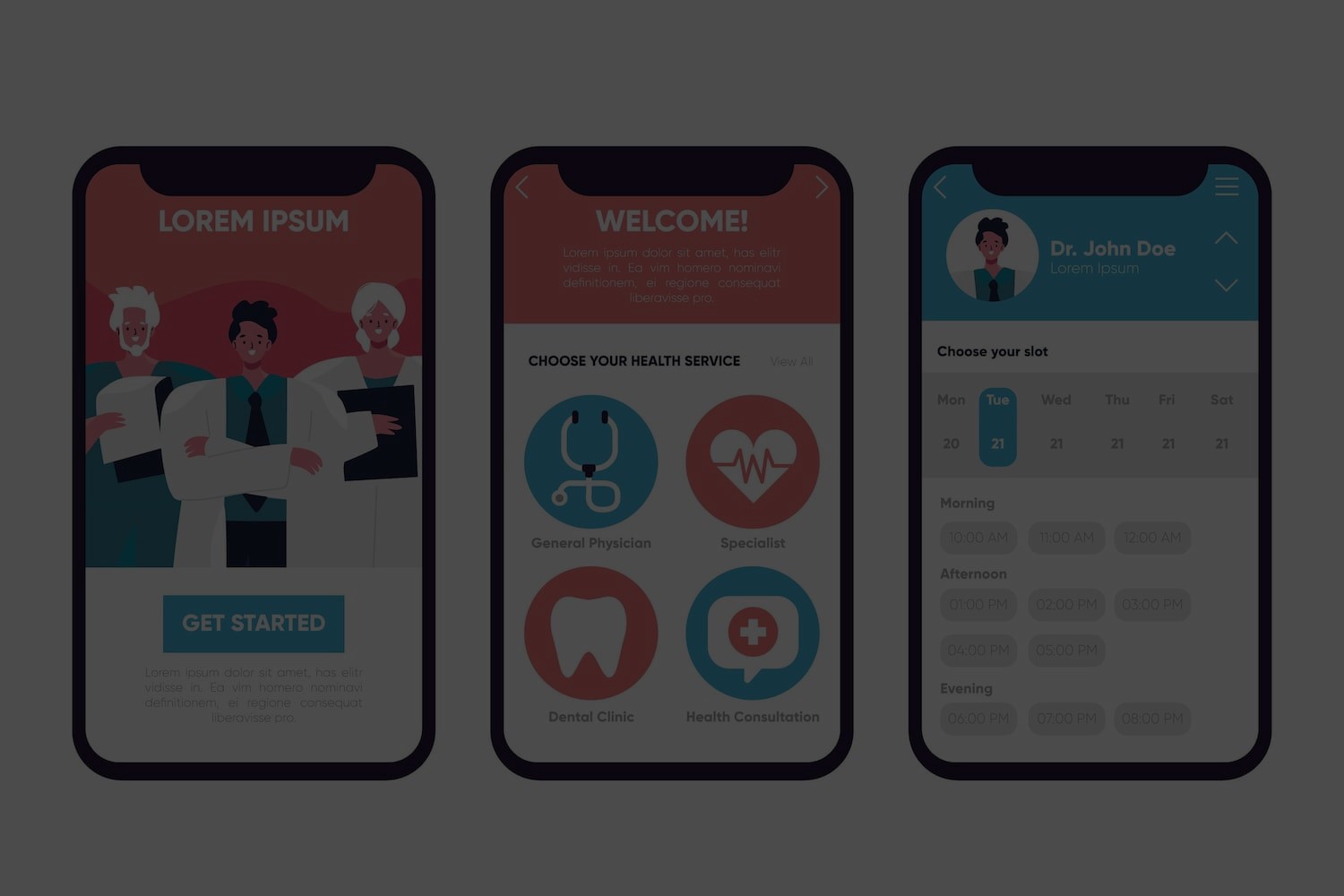

Mobile apps play a crucial role in improving patient care and enabling
more efficient and safe clinical workflows. They also support the
management of health information for patients and health professionals
and efficiently fulfill diverse care needs. In many health settings
constrained by limited resources, apps facilitate access to medical
expertise and information. Given the far-reaching impact of apps on
healthcare, clinical developers have increasingly assigned user
interface (UI) and user experience (UX) design a pivotal position in
the development life-cycle. It will fail if a mobile health (mHealth)
app doesn’t meet users’ expectations.
It guides how the content is laid out to make sure it’s aesthetically
appealing and easy to navigate – a visually appealing and handy
structure. Good UX design can also do things such as track common
paths that users take to navigate between areas of the app or
anticipate another action someone may take by placing a helpful button
on another screen. UI design and good UX design both make the app
effective, usable, and efficient for people to use. For healthcare
apps that rely on people understanding what the app is asking them and
effortlessly engaging in those actions, good UI and UX design is
vital. They impact the extent to which a person is satisfied with
using it, how much they’ll use the app, how easy it will be to use,
and, ultimately, whether the app is successful in helping a person
achieve their desired health outcome.
By incorporating thoughtful design into healthcare apps, patient
experience, workflow, and outcomes can be drastically enhanced. In
this article, we will explore design tenets that can make healthcare
applications easy, friendly, and impactful for users.
Interfaces designed with users in mind can improve interactions and
help ensure users get the most out of the app. Interfaces that
incorporate attention to simple usability principles—ease,
consistency, and accessibility—can be intuitive and user-friendly and
help patients, clinicians, and caregivers reach their health and
wellness goals through measurable improvements in human interaction.
Proper design can ensure that users know where they are within an app,
can access important data easily, and are not metaphorical tramps in a
digital diner.
By collecting user feedback through iterative tests and using an
iterative design process, the app can be continuously improved and
evolve to meet users’ needs and expectations over time. With these
design aspects prioritized, health apps can achieve higher user
satisfaction, produce better health outcomes, and have a stronger
impact on modern healthcare.
Privacy Policy
© 2025 All Rights Reserved